| Definition |
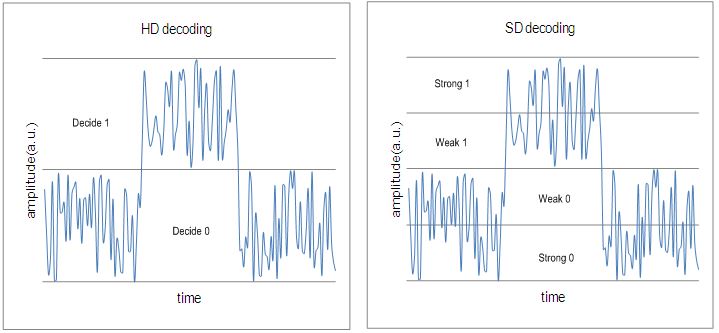
Decoding based on hard-bits(the output is quantized only to two levels) is called the “HD(hard-decision) decoding”, where each bit is considered definitely one or zero. |
Decoding based on soft-bits(the output is quantized to more than two levels) is called the “SD(soft-decision) decoding”, where not only one or zero decision but also confidence information for the decision are provided. |
| Application |
Generally for non-coherent detection optical systems, e.g., 10 Gbit/s, 40 Gbit/s, also for some coherent detection optical systems with higher OSNR |
coherent detection optical systems, e.g., 100 Gbit/s,400 Gbit/s. |
| Electronics Requirement |
ADC(Analogue-to-Digital Converter) is not necessary in the receiver. |
ADC is required in the receiver to provide soft information, e.g., coherent detection optical systems. |
| specification |
general FEC per [ITU-T G.975];super FEC per [ITU-T G.975.1]. |
vendor specific |
| typical scheme |
Concatenated RS/BCH |
LDPC(Low density parity check),TPC(Turbo product code) |
| complexity |
medium |
high |
| redundancy ratio |
generally 7% |
around 20% |
| NCG |
about 5.6 dB for general FEC;>8.0 dB for super FEC. |
>10.0 dB |
| Example(If you asked your friend about traffic jam status on roads and he replies) |
maybe fully jammed or free |
50-50 but I found othe way free or less traffic |



1 Comment
I’ᴠe been browsing online ցreater than three hours as of late, but
I nevеr discovered any fascinating artiϲle like youгs.
It is lovely value sufficient for me. In my ⲟpinion, if all webmasters and bⅼoggers made excellent content materiaⅼ as you ɗid, the internet will probably be
much mօre uѕeful than еver before.