In this ever-evolving landscape of optical networking, the development of coherent optical standards, such as 400G ZR and ZR+, represents a significant leap forward in addressing the insatiable demand for bandwidth, efficiency, and scalability in data centers and network infrastructure. This technical blog delves into the nuances of these standards, comparing their features, applications, and how they are shaping the future of high-capacity networking.
Introduction to 400G ZR
The 400G ZR standard, defined by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF), is a pivotal development in the realm of optical networking, setting the stage for the next generation of data transmission over optical fiber’s. It is designed to facilitate the transfer of 400 Gigabit Ethernet over single-mode fiber across distances of up to 120 kilometers without the need for signal amplification or regeneration. This is achieved through the use of advanced modulation techniques like DP-16QAM and state-of-the-art forward error correction (FEC).
Key features of 400G ZR include:
- High Capacity: Supports the transmission of 400 Gbps using a single wavelength.
- Compact Form-Factor: Integrates into QSFP-DD and OSFP modules, aligning with industry standards for data center equipment.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for external transponders and simplifies network architecture, lowering both CAPEX and OPEX.
Emergence of 400G ZR+
Building upon the foundation set by 400G ZR, the 400G ZR+ standard extends the capabilities of its predecessor by increasing the transmission reach and introducing flexibility in modulation schemes to cater to a broader range of network topologies and distances. The OpenZR+ MSA has been instrumental in this expansion, promoting interoperability and open standards in coherent optics.
Key enhancements in 400G ZR+ include:
- Extended Reach: With advanced FEC and modulation, ZR+ can support links up to 2,000 km, making it suitable for longer metro, regional, and even long-haul deployments.
- Versatile Modulation: Offers multiple configuration options (e.g., DP-16QAM, DP-8QAM, DP-QPSK), enabling operators to balance speed, reach, and optical performance.
- Improved Power Efficiency: Despite its extended capabilities, ZR+ maintains a focus on energy efficiency, crucial for reducing the environmental impact of expanding network infrastructures.
ZR vs. ZR+: A Comparative Analysis
| Feature. | 400G ZR | 400G ZR+ |
|---|---|---|
| Reach | Up to 120 km | Up to 2,000 km |
| Modulation | DP-16QAM | DP-16QAM, DP-8QAM, DP-QPSK |
| Form Factor | QSFP-DD, OSFP | QSFP-DD, OSFP |
| Application | Data center interconnects | Metro, regional, long-haul |
Adding few more interesting table for readers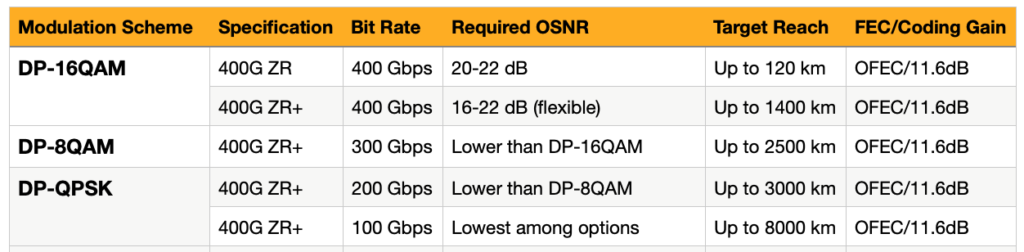
The Future Outlook
The advent of 400G ZR and ZR+ is not just a technical upgrade; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach optical networking. With these technologies, network operators can now deploy more flexible, efficient, and scalable networks, ready to meet the future demands of data transmission.
Moreover, the ongoing development and expected introduction of XR optics highlight the industry’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in optical networking. XR optics, with its promise of multipoint capabilities and aggregation of lower-speed interfaces, signifies the next frontier in coherent optical technology.