HomePosts tagged “bitrate”
bitrate
Showing 1 - 2 of 2 results
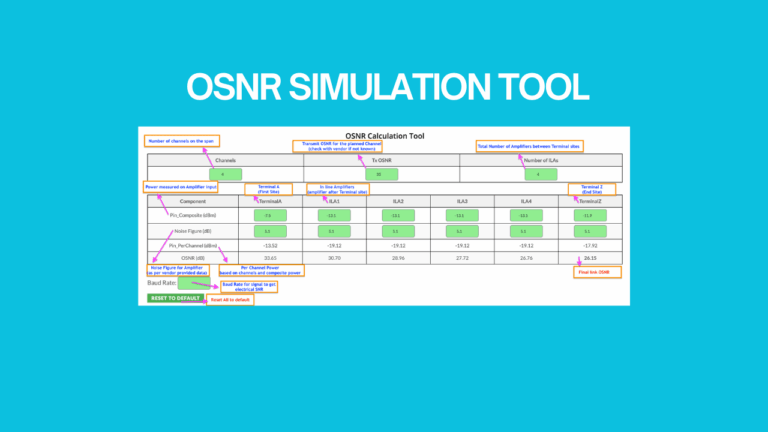
Based on my experience ,I have seen that Optical Engineers need to estimate Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR) often specially when...
-
Free
-
March 26, 2025
Bit rate Vs Baud rate in Optical Network Bit rate Vs Baud rate in Optical Network A Comprehensive Guide to...
-
Free
-
March 26, 2025
Explore Articles
Filter Articles
ResetExplore Courses
Tags
automation
ber
Chromatic Dispersion
coherent optical transmission
Data transmission
DWDM
edfa
EDFAs
Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers
fec
Fiber optics
Fiber optic technology
Forward Error Correction
Latency
modulation
network automation
network management
Network performance
noise figure
optical
optical amplifiers
optical automation
Optical communication
Optical fiber
Optical network
optical network automation
optical networking
Optical networks
Optical performance
Optical signal-to-noise ratio
Optical transport network
OSNR
OTN
Q-factor
Raman Amplifier
SDH
Signal amplification
Signal integrity
Signal quality
Slider
submarine
submarine communication
submarine optical networking
Telecommunications
Ticker