- What is DWDM technology?
A: DWDM stands for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, a technology used in optical networks to increase the capacity of data transmission by combining multiple optical signals with different wavelengths onto a single fiber.
- How does DWDM work?
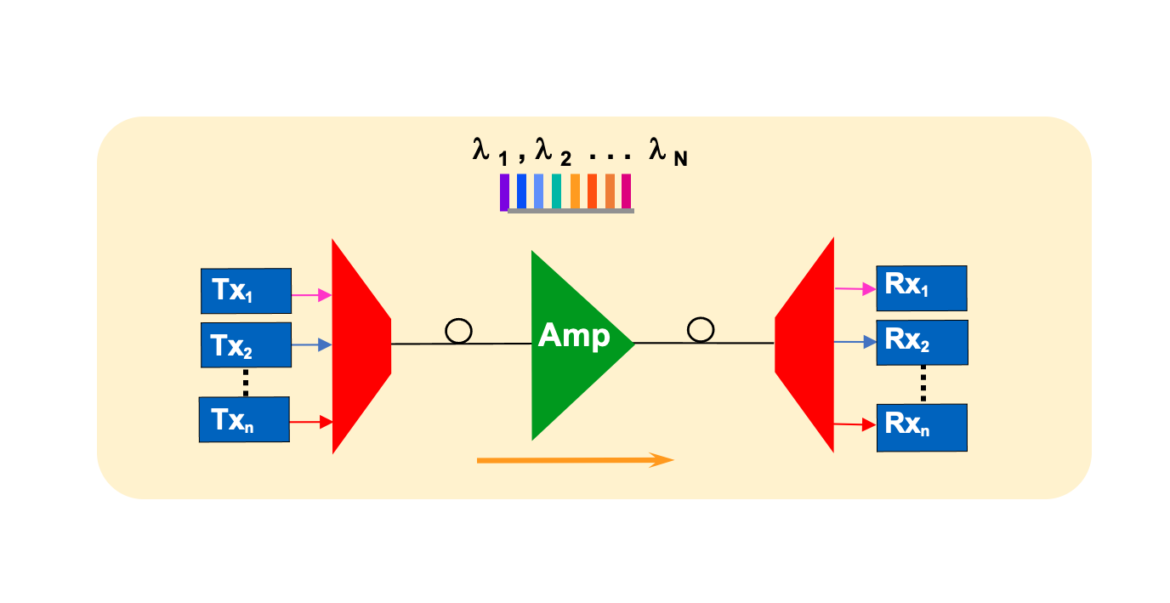
A: DWDM works by assigning each incoming data channel a unique wavelength (or color) of light, combining these channels into a single optical fiber. This allows multiple data streams to travel simultaneously without interference.
- What is the difference between DWDM and CWDM?
A: DWDM stands for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing, while CWDM stands for Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. The primary difference is in the channel spacing, with DWDM having much closer channel spacing, allowing for more channels on a single fiber.
- What are the key components of a DWDM system?
A: Key components of a DWDM system include optical transmitters, multiplexers, optical amplifiers, de-multiplexers, and optical receivers.
- What is an Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer (OADM)?
A: An OADM is a device that adds or drops specific wavelengths in a DWDM system while allowing other wavelengths to continue along the fiber.
- How does DWDM increase network capacity?
A: DWDM increases network capacity by combining multiple optical signals with different wavelengths onto a single fiber, allowing for simultaneous data transmission without interference.
- What is the typical channel spacing in DWDM systems?
A: The typical channel spacing in DWDM systems is 100 GHz or 0.8 nm, although more advanced systems can achieve 50 GHz or even 25 GHz spacing.
- What is the role of optical amplifiers in DWDM systems?
A: Optical amplifiers are used to boost the signal strength in DWDM systems, compensating for signal loss and enabling long-distance transmission.
- What is the maximum transmission distance for DWDM systems?
A: Maximum transmission distance for DWDM systems varies depending on factors such as channel count, fiber type, and amplification. However, some systems can achieve distances of up to 2,500 km or more.
- What are the primary benefits of DWDM?
A: Benefits of DWDM include increased network capacity, scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- What are some common applications of DWDM technology?
A: DWDM technology is commonly used in long-haul and metropolitan area networks (MANs), as well as in internet service provider (ISP) networks and data center interconnects.
- What is a wavelength blocker?
A: A wavelength blocker is a device that selectively blocks or filters specific wavelengths in a DWDM system.
- What are erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs)?
A: EDFAs are a type of optical amplifier that uses erbium-doped fiber as the gain medium, providing amplification for DWDM systems.
- How does chromatic dispersion impact DWDM systems?
A: Chromatic dispersion is the spreading of an optical signal due to different wavelengths traveling at different speeds in the fiber. In DWDM systems, chromatic dispersion can cause signal degradation and reduce transmission distance.
- What is a dispersion compensating module (DCM)?
A: A DCM is a device used to compensate for chromatic dispersion in DWDM systems, improving signal quality and transmission distance.
- What is an optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR)?
A: OSNR is a measure of the quality of an optical signal in relation to noise in a DWDM system. A higher OSNR indicates better signal quality.
- How does polarization mode dispersion (PMD) affect DWDM systems?
A: PMD is a phenomenon where different polarization states of
ight travel at different speeds in the fiber, causing signal distortion and degradation in DWDM systems. PMD can limit the transmission distance and data rates.
- What is the role of a dispersion management strategy in DWDM systems?
A: A dispersion management strategy helps to minimize the impact of chromatic dispersion and PMD, ensuring better signal quality and longer transmission distances in DWDM systems.
- What is a tunable optical filter?
A: A tunable optical filter is a device that can be adjusted to selectively transmit or block specific wavelengths in a DWDM system, allowing for dynamic channel allocation and reconfiguration.
- What is a reconfigurable optical add-drop multiplexer (ROADM)?
A: A ROADM is a device that allows for the flexible addition, dropping, or rerouting of wavelength channels in a DWDM system, enabling dynamic network reconfiguration.
- How does DWDM support network redundancy and protection?
A: DWDM can be used to create diverse optical paths, providing redundancy and protection against network failures or service disruptions.
- What is the impact of nonlinear effects on DWDM systems?
A: Nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation, cross-phase modulation, and four-wave mixing can cause signal degradation and limit transmission performance in DWDM systems.
- What is the role of forward error correction (FEC) in DWDM systems?
A: FEC is a technique used to detect and correct errors in DWDM systems, improving signal quality and transmission performance.
- How does DWDM enable optical network flexibility?
A: DWDM allows for the dynamic allocation and reconfiguration of wavelength channels, providing flexibility to adapt to changing network demands and optimize network resources.
- What is the future of DWDM technology?
A: The future of DWDM technology includes continued advancements in channel spacing, transmission distances, and data rates, as well as the integration of software-defined networking (SDN) and other emerging technologies to enable more intelligent and adaptive optical networks.



Comments are closed.