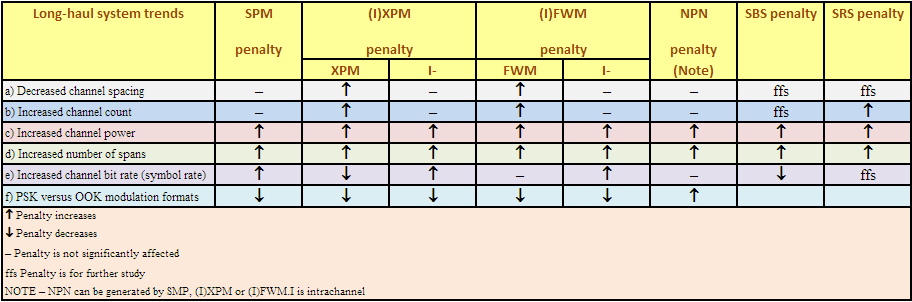
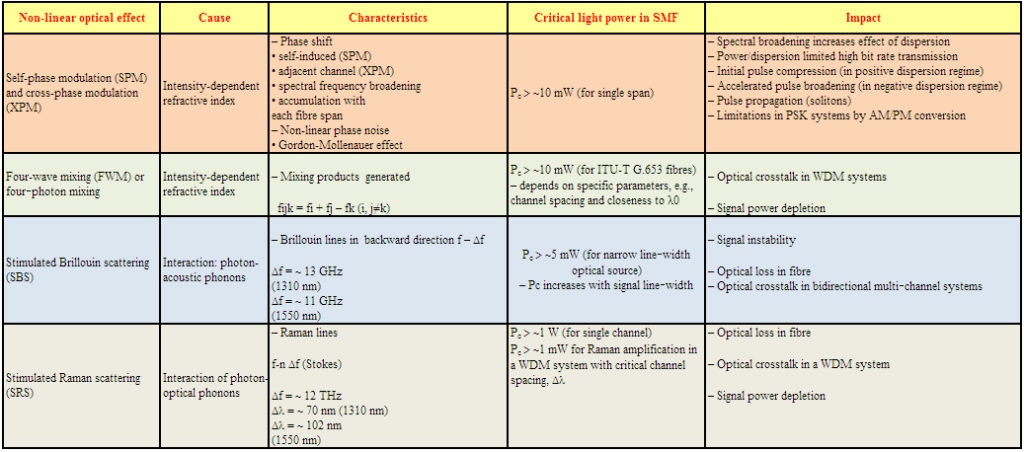
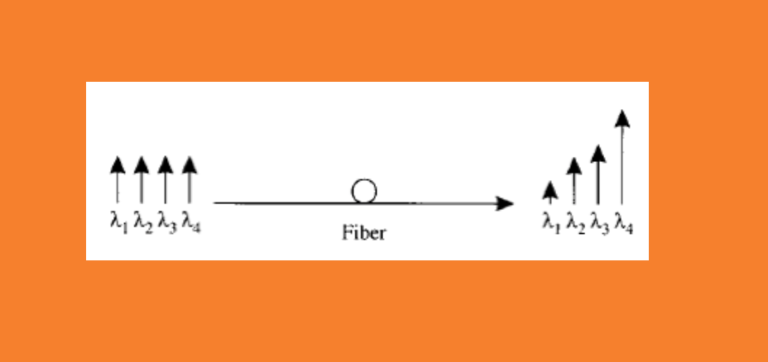
Non-linear interactions between the signal and the silica fibre transmission medium begin to appear as optical signal powers are increased to achieve longer span lengths at high bit rates. Consequently, non-linear fibre behaviour has emerged as an important consideration both in high capacity systems and in long unregenerated routes. These non-linearities can be generally categorized as either scattering effects (stimulated Brillouin scattering and stimulated Raman scattering) or effects related to the fibre’s intensity dependent index of refraction (self-phase modulation, cross-phase modulation, modulation instability, soliton formation and four-wave mixing). A variety of parameters influence the severity of these non-linear effects, including line code (modulation format), transmission rate, fibre dispersion characteristics, the effective area and non-linear refractive index of the fibre, the number and spacing of channels in multiple channel systems, overall unregenerated system length, as well as signal intensity and source line-width. Since the implementation of transmission systems with higher bit rates than 10 Gbit/s and alternative line codes (modulation formats) than NRZ-ASK or RZ-ASK, described in [b-ITU-T G-Sup.39], non‑linear fibre effects previously not considered can have a significant influence, e.g., intra‑channel cross-phase modulation (IXPM), intra-channel four-wave mixing (IFWM) and non‑linear phase noise (NPN).